
The parathyroid glands are the smallest organs of the human body, located on anterior side of the neck, just behind the thyroid gland. Parathyroid glands keep blood calcium levels within the normal range. The level of blood calcium is decrease when the parathyroid glands hypofunctioning (hypoparathyroidism) and the level of blood calcium is increase when the glands hyperfunctioning (hyperparathyroidism). Both situations cause severe complaints and dysfunctions in many organs, particularly the heart, kidney, and vascular structures.

Parathyroid transplantation is an organ transplantation process, but since the size of the parathyroid glands are small, the transplantation process has some unique differences.
There are two main techniques in parathyroid transplantation: Tissue transplantation and cell transplantation
Parathyroid transplantation is performed only to persons with a diagnosis of permanent hypoparathyroidism.

Permanent hypoparathyroidism means that parathormone (PTH) and calcium levels in the blood are low at least six months with the symptoms of hypocalcemia (muscle contractions, tremors, fatigue, etc.)

There are two treatment options except transplantation in permanent hypoparathyroidism:
1- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation (called as classical treatment): This treatment option should be continued for lifelong. Calcium pills may cause duodenal and gastric ulcer wounds and may cause kidney damages via accumulation in the kidney when used for a long time. Moreover, this approach does not cure the disease itself, it ensure only temporarily to raise the low calcium level in the blood.
2- Recombinant parathormone (r-PTH) treatment: r-PTH is the biosmilar product of the natural parathormone (PTH). It is applied as a subcutaneous injection with small needles just like the application of insulin in diabetic patients. r-PTH injection is more effective than classical treatment and side effect potential is low but this treatment option is more expensive than classical treatment.
Thyroid (goiter) surgery is one of the most frequent operation in endocrine diseases. Because of the blood vessels of the thyroid gland is very intense and the thyroid tissue is very close to serious anatomical structures (like voice nerves, parathyroid glands, carotid artery) goiter surgery is a serious and difficult operation category. The parathyroid glands may damage during thyroid surgery because of they are very small and attached to the thyroid gland at the posterior side. Parathyroid gland damage during thyroid surgery is a rare complication, but when it occurs the condition is serious and unfortunately no definite treatment option other than parathyroid transplantation.
Three groups of people may have a donor for permanent hypoparathyroidism patients:
- Brain deaths people with donated of organs. These are called as cadaveric donors.
- Excessive parathyroid hyperplasia cases that requires surgery due to renal failure.
- Healthy people (especially first degree relationship of the patient) who have similar blood and tissue groups of the patient.
Like lots type of surgical approaches successful parathyroid surgery is related to experience of the surgeon. If the surgical approaches perform carefully with experienced endocrine surgeon donor don’t suffer any damages.
No any age limits for parathyroid transplantation. If the patient is diagnosed as permanent hypoparathyroidism, transplantation can be performed in any ages.
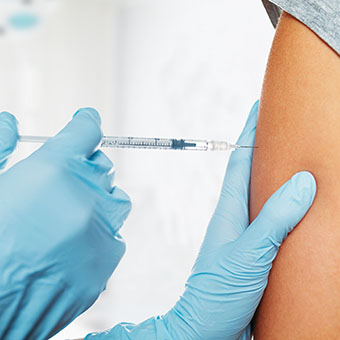 Parathyroid transplant is an intramuscular injection. The patient does not enter the operating room, does not receive anesthesia, no incision is made on his body, no stitches. The parathyroid cells previously taken from the donor. The cells are prepared for transplantation under special and sterile laboratory conditions. Cells put into a standard injector in a special liquid of 2ml and injected into the patient’s arm or abdominal muscles. This application is performed at the patient’s bedside not in the operation room and takes only a few seconds. After the procedure, the patient is observed for a few hours and then discharged. There is no need to stay in the hospital for night. Drugs that suppress the body’s defense system (immunosuppressant drugs) are not used after the transplantation.
Parathyroid transplant is an intramuscular injection. The patient does not enter the operating room, does not receive anesthesia, no incision is made on his body, no stitches. The parathyroid cells previously taken from the donor. The cells are prepared for transplantation under special and sterile laboratory conditions. Cells put into a standard injector in a special liquid of 2ml and injected into the patient’s arm or abdominal muscles. This application is performed at the patient’s bedside not in the operation room and takes only a few seconds. After the procedure, the patient is observed for a few hours and then discharged. There is no need to stay in the hospital for night. Drugs that suppress the body’s defense system (immunosuppressant drugs) are not used after the transplantation.
After the transplantation, the patient is stay in the hospital for a few hours only. After this observation period patient is discharged. After the transplantation there are no special diet and no any serious restrictions of life. It may take several weeks for the functioning of the transplanted cells so patients must be take routine medications similar the pre-transplantation period. Patients are followed up with a blood tests for 30 day periods in the post-transplantation period. The medications are release gradually.
.
There is no 100% success rate of any organ transplantations in the world. Moreover, the success of each organ transplants depends on many factors, such as the donor and recipient ages, the quantity and variety of surface antigens of the transplanted cells, the power of the recipient’s immune system, the functional capacity of the cells, the correct application of laboratory techniques, etc. These factors are also eligable for the success of the parathyroid transplantation.
When transplantation is not successful in solid organ transplantations (kidney, liver, etc.), the transplanted organ must be removed from the body. This means a new surgical procedure. But new surgical access is not necessary for parathyroid transplantation. If the parathyroid transplantation is failed this means that the transplanted cells is destroyed, digested by the host immune system cells. So no surgical intervention is required and no side effects occur for this cases.
Yes. Whether the first transplantation is successful and over the years the cells have lost functionality or the first transplantation is failed, re-transplantation may be used for these cases.
